Common communication protocols in the Internet of Things
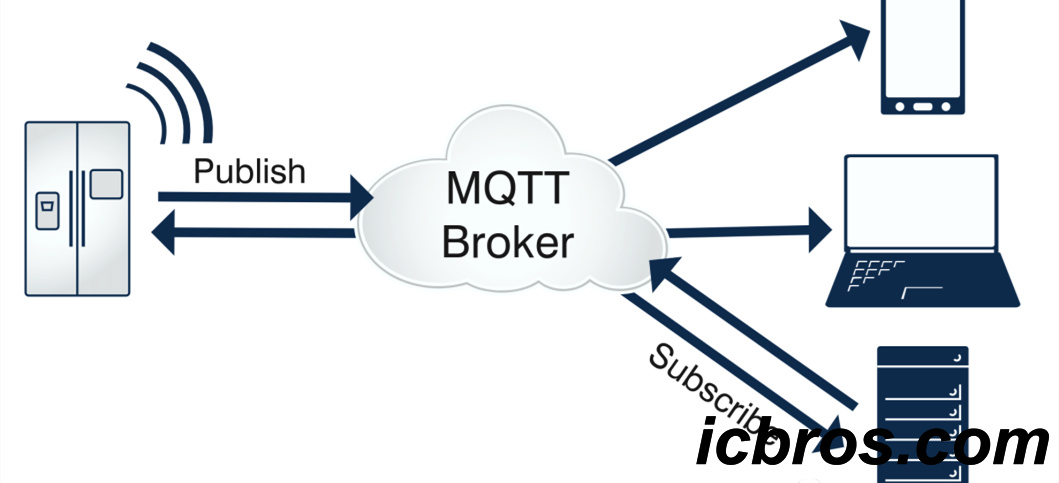
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a common protocol in Internet of Things (IoT) communication. It is a lightweight messaging protocol widely used for communication between devices and servers.
The working principle of the MQTT protocol is similar to a publish subscribe model, which allows different devices or clients to exchange messages through a middleware called a broker. The device or client can choose to subscribe to a specific topic and receive messages from the agent. At the same time, devices or clients can also publish messages to one or more specific topics, and the agent will forward these messages to all devices or clients that subscribe to the topic.
Compared to other communication protocols, the MQTT protocol has the following advantages:
1. It is a lightweight protocol that consumes very little bandwidth and resources;
2. It has high reliability and can ensure the transmission and reception of messages;
3. It supports Asynchronous communication and offline messages, and can receive and send messages even if the device is not online.
Therefore, MQTT protocol is the most commonly used protocol in IoT applications, which can help devices communicate efficiently and provide a reliable and secure messaging mechanism for IoT applications.
When we talk about IoT communication protocols, CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) is a very important protocol. CoAP is a resource oriented protocol designed for limited devices and network environments to achieve low-power, low bandwidth, and low latency communication.
In short, CoAP is a reliable and efficient Internet of Things communication protocol that can help devices communicate in low-power, low bandwidth, and low latency environments, and can interact with other devices by querying resource status, triggering events, and other means.
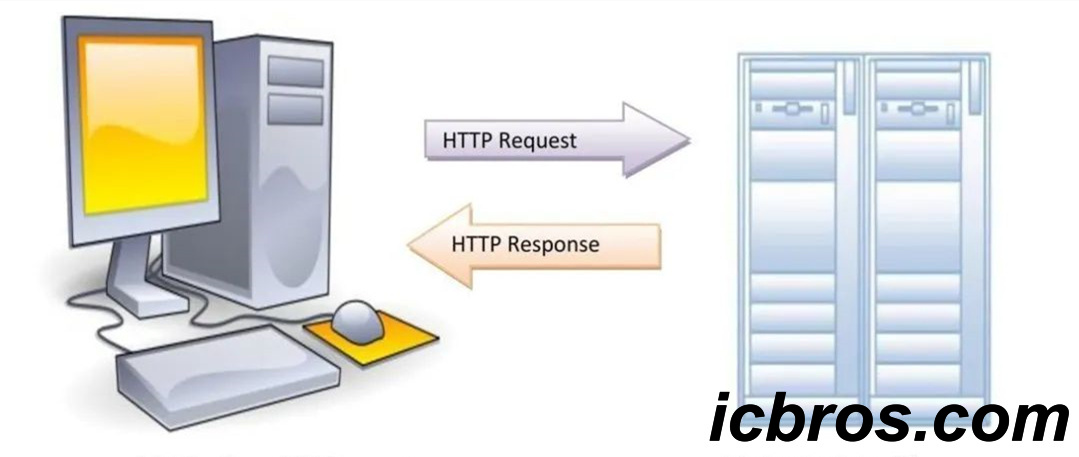
HTTP is a reliable and flexible Internet of Things communication protocol that helps devices communicate over the Internet and supports various data formats and communication methods. However, when using HTTP, attention needs to be paid to issues such as power consumption and latency to ensure that the device can function properly in low-power, low bandwidth, and low latency environments.
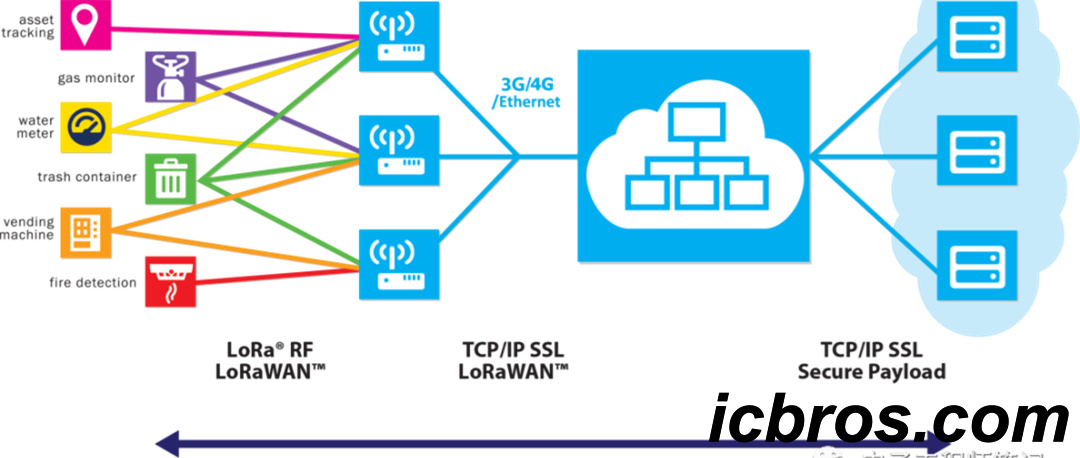
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a wireless communication protocol designed specifically for IoT devices. It has the following characteristics:
1. Long distance: LoRaWAN can communicate within a range of several kilometers or even tens of kilometers.
2. Low power consumption: It uses low-power technology to enable devices to operate continuously for several years.
3. Bidirectional communication: LoRaWAN supports bidirectional communication and can receive data from devices and send instructions to them.