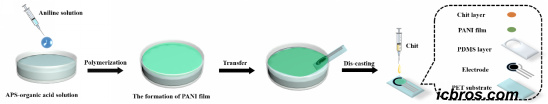
A sweat electrochemical sensor for non-invasive tracking of vitamin C concentration in human body fluids
Nutrition monitoring plays an important role in maintaining human health and preventing diseases. Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is an essential nutrient in the human body that can enhance immunity and promote wound recovery after surgery. The vitamin C content in healthy human serum is 50 μ M~70 μ M. The concentration in sweat is 10 μ M~50 μ M. Proper intake of vitamin C can promote human health. Lack of vitamin C in the body may lead to diseases such as scurvy, muscle weakness, skin and gum bleeding, while excessive vitamin C may lead to kidney stones, nausea, diarrhea, and other diseases. Therefore, developing high-performance and reliable sensors for rapid monitoring of vitamin C is of great significance for public health care.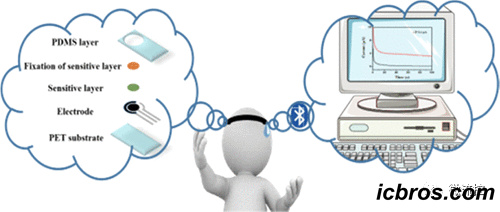
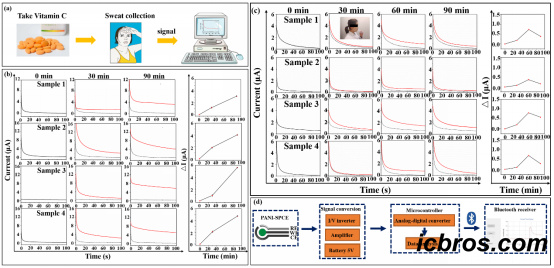
Saliva is an easily obtainable body fluid with broad application prospects in on-site testing. Therefore, saliva should be monitored after taking vitamin C. The collected saliva samples have not undergone any processing and are directly used for testing. The results showed that the response current value gradually decreased after 60 minutes. The time of the maximum response current in saliva is different from that in sweat, as vitamin C molecules are excreted from plasma to different bodily fluids through different metabolic pathways (Figure 2). The above results indicate that the sensor has certain application potential in personalized nutrition guidance.
In order to enhance the practicality of the sensor, researchers have designed a portable vitamin C detection system. Figure 3 shows a photo of the portable vitamin C sensor and integrated circuit module. The portable sensor consists of two parts: signal conversion and microcontroller, which are then transmitted to the computer through wireless Bluetooth devices. Subsequently, a Java based application was developed for manipulating and displaying results. Although there are some deviations in the monitoring system, the overall trend is consistent with previous test results. This two-dimensional PANI thin film sensor based detection system has certain potential for monitoring vitamin C in daily life.
In summary, researchers have designed a sweat electrochemical sensor for non-invasive tracking of vitamin C concentration in human body fluids. The highly symmetrical circular structure of phytic acid enhances electron transfer between PANI chains, and it has a more carboxyl group structure, making the film have more catalytic sites, thereby improving the sensor's sensing performance against ascorbic acid. At the same time, the PANI thin film sensor can also be used to detect changes in vitamin C content in untreated sweat and saliva after intake of vitamin C. Different test subjects exhibit different response currents after consuming a quantitative amount of vitamin C, which may be due to differences in personal metabolism, weight, dietary habits, and other factors. The pharmacological tracking characteristics of this sensor reflect its potential application in nutritional guidance.
ICBROS TECHNOLOGY LIMITED is a worldwide professional electronic components distributor.
Web:https://www.icbros.com
Email:service@icbros.com
#DAC #pcbuild #icbros #analogelectronics #semimodular #preamplifier #elettronica #supercon #pcbengineer #diyelectronics #eletricistas #emeddedsystems #hobielektronik #electricalprojects #components #makers #engineering #irremote #studentproject #pic24 #eletronica #drscientist #universalrobots #circuitplayground #powersupply #arduinocompatible